Gastroenteritis In Children: Everything You Need To Know

In this article, we share important facts about gastroenteritis in children, commonly referred to as gastritis or vomiting.
The symptoms of this gastrointestinal inflammation can sometimes be confused with simple stomach pain. However, if the child’s symptoms are accompanied by certain signs and they last for a long time, the child may have gastroenteritis, which is characterized by cramps, diarrhea and vomiting.
Common symptoms of gastroenteritis in children
The clinical manifestations of gastroenteritis are characterized by large amounts of diarrhea. Stomach pain and vomiting are also common symptoms. Although vomiting is common, it does not occur in all children.
Nausea and fever may also occur. Children suffering from gastroenteritis may also get skin irritation around the anus. Keep in mind that children can react to the disease in different ways.
Sometimes the condition disappears on its own, but it is important to observe the child to prevent complications such as increased fever and dehydration. These can have a serious impact on the child’s health.
Causes
Gastroenteritis can have many different causes. If the child has abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting, it may be due to a virus. However, there are other reasons as well.
Gastroenteritis in children can be caused by viruses such as rotavirus and adenovirus. But bacteria such as salmonella and campylobacter can also cause the above symptoms. In addition, the condition can be caused by the baby’s diet, inflammatory diseases and other medical conditions.
Causes that are less common in children are ulcerative colitis, hyperthyroidism and Crohn’s disease.
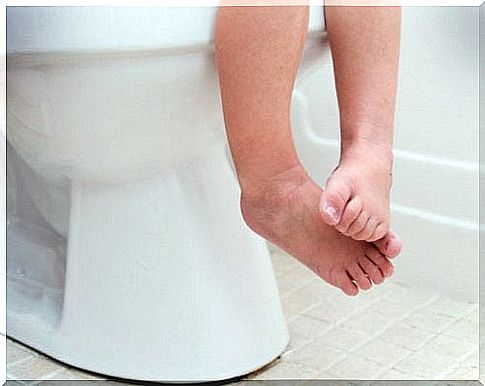
Types of gastroenteritis in children
The child’s diarrhea can provide clues as to the cause of the stomach illness. For example, if the disease is due to bacteria from eating food that has become bad, the baby’s diarrhea will be largely fluid. The child may also need to go to the toilet often.
If the stomach disease is due to salmonella, the diarrhea is usually a little more severe and is accompanied by mucus. The child may feel sick and have a fever.
Actions
If a child vomits, it is best to wait at least 60 to 90 minutes before feeding or giving the child any fluids. This prevents the intestine from becoming more irritated. Parents can take this action as long as the child is not dehydrated.
There are medications and foods that are good for getting more fluids in children. Fluid replacement can be given orally or intravenously.
If your child has diarrhea for more than 3 days, contact your doctor immediately. You should do the same if your child suffers from dehydration or has an uncontrollable fever.
How do you know if your baby is dehydrated?
The amount of fluid that comes out, as well as how long the little one goes without eating, gives clues about the intensity of dehydration. But the baby’s body can also give clear signals.

The most obvious signs of dehydration are dry mouth and lips, decay, pale or whitish skin, dark circles around the eyes and little urine production. If you notice any of these signs, give water to the baby.
While a child is suffering from gastroenteritis, he or she should avoid citrus juice.
Take care of the baby’s diet during and after the illness
It is important to think about what the child ingests for nutrition during and after gastroenteritis. Try to avoid f banquets and fried food during the time the child is experiencing symptoms and in a few days after they disappeared.
Dairy products and sweets are also not recommended as they can irritate the intestines. Gastroenteritis in children can usually be treated with a healthy diet.
When the stomach disease is gone, you will notice that the baby’s appetite returns immediately.