What Is An Amniocentesis And What Are The Risks?
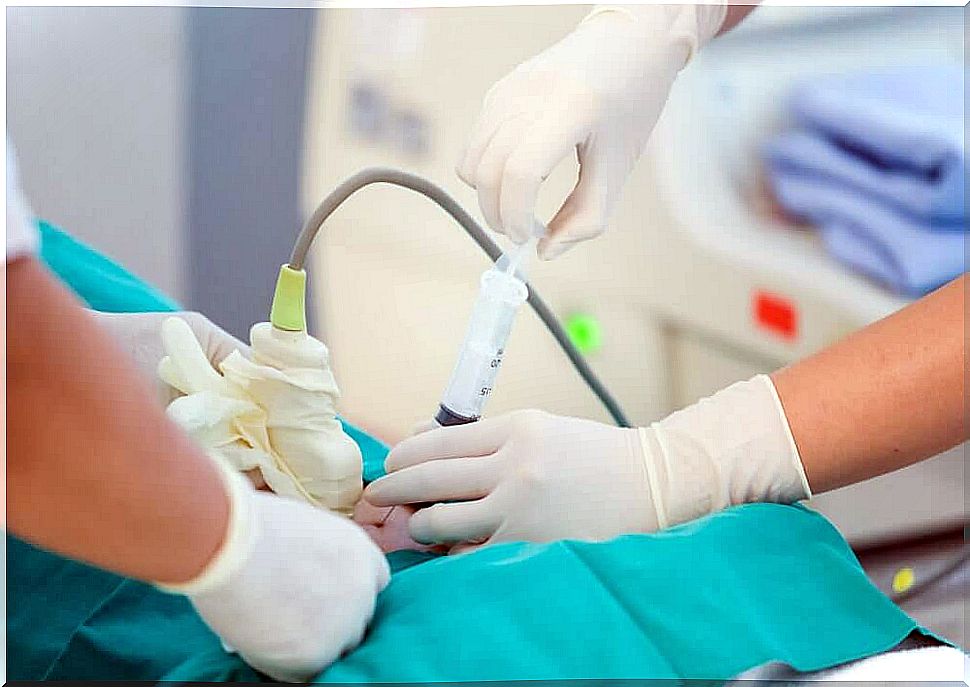
An amniocentesis is a medical procedure in which some amniotic fluid is sucked out through a needle to analyze a child’s chromosomes.
The test is usually performed between weeks 16 and 20, and is recommended for women who are 35 years and older.
The amniotic fluid consists of cells, protein and urine from the fetus. All this can be analyzed to obtain information about the baby’s health.
The cells and the protein are examined in a laboratory to find out if there is anything wrong with the fetus. The amniotic fluid also contains alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) which is measured in a lab.
The sampling lasts for about 45 minutes and during most of the time the fetus is examined with ultrasound.
Why take an amniocentesis?
The study can detect Down’s syndrome up to 99%. It can also show other genetic problems and chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, including anacephaly (when the child lacks a large part of the brain).
Amniocentesis is also used to detect unusual metabolic problems that children inherit from their parents, as well as other genetic abnormalities such as Trisomy 18.
An amniocentesis can also show if the baby is suffering from a malformation of the neural tube, such as spina bifida, or certain metabolic diseases.
The test also allows you to detect infections in the uterus and fetal anemia.
Alternative fetal diagnostics
Gynecologists now offer an alternative to taking amniocentesis by taking a blood sample instead.
Instead, it only evaluates the risk of the child getting Down syndrome, Edward’s syndrome or Patau’s syndrome, as well as the presence or absence of extra chromosomes. You can also find out the child’s gender.
The problem with this test, when compared to amniocentesis, is how reliable it is. Amniocentesis is much more accurate and reliable.
Parents often have mixed feelings about taking an amniocentesis: they want to know the results, but do not want to expose the child to any risk.
Specialists recommend that before going through the test, think about the consequences of a result that shows that the child has Down syndrome.
What does an amniocentesis consist of?
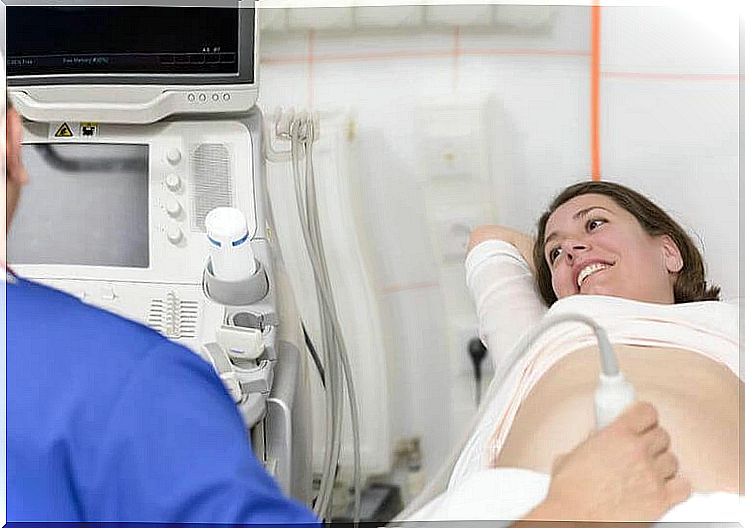
When a woman is 35 years or older and undergoes an amniocentesis, a specialist will extract small amounts of the amniotic fluid.
To be able to do this, a thin needle is inserted into the uterus through the stomach and sucks out some of the fluid, while using ultrasound to make sure that you stick the needle in the right place.
It is a quick and fairly painless examination, and the older the woman, the more necessary it is because the risk of the child being born with chromosomal abnormalities then also increases.
However, many women around the world are still afraid to undergo the survey because it has been shown that it can increase the risk of miscarriage.
Studies have shown that one in 1,600 women suffers a miscarriage as a result of amniocentesis. However, it is still the most reliable sample available.
Specialists insist it is not painful. So far, it has only been seen that some women experience some discomfort from the needle. Others experience mild cramps during and after the procedure, but it often disappears quickly.
The seizures usually disappear within an hour, but can recur periodically for one to two days.
Some women may also experience abdominal pain where the needle has been inserted, which usually disappears within a few hours, but can also last for several days.









