What To Do If Your Child Has Molluscum Contagiosum (MC)
Molluscum contagiosum, also called just mollusks, is a fairly common viral infection in children. It gives characteristic skin rashes. No matter how long the outbreak lasts, it is a benign infection. In this article, we will provide information and tips that can help you if your child suffers from it.
What is molluscum contagiosum (MC)?
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), which is a POX virus. As children’s immune systems are not yet fully developed, they are the population group most affected by this condition.
In Europe, it affects up to 5% of children between the ages of two and 12. So it is a fairly common infection. The virus affects the mucous membranes and the most superficial layers of the skin.
It can spread as follows:
- Direct contact with people who suffer from it, such as skin contact.
- Through objects that people with molluscum contagiosum have used and infected, such as toys, towels and clothes.
- It can spread to other body parts of a person who already has an infection.
What are the symptoms of mollusks?
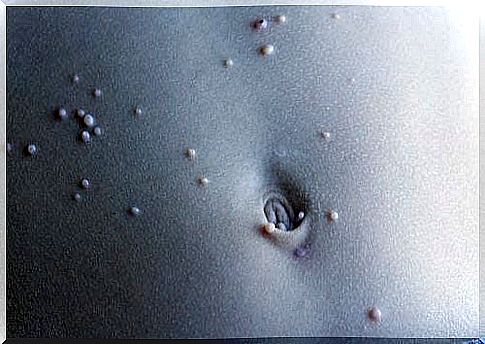
The virus causes skin lesions. These are similar to small round and raised pimples or warts and they contain the virus. They may have a pit in the middle. In general, these mollusks usually occur in areas such as the armpits, armpits or groin, but they can affect any part of the body.
Molluscum contagiosum lesions may occur alone or in groups. Although they do not usually cause pain, they usually itch. In fact, the virus spreads easily to other parts of the body when you tear and itch. If the affected person really has a very troublesome itching and he or she tears, major injuries can occur.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
As always, a doctor will need to diagnose this skin condition. Usually no tests are needed. For the most part, a doctor can diagnose mollusks with the naked eye.
As I said, the virus is usually a benign disease that, although it can take months and sometimes years to disappear, usually disappears without any treatment.
However, there are still some treatments that can help fight the infection, for example:
- Empty the mollusks of their viral contents by squeezing it out with a suitable material.
- Freezing of lesions (cryotherapy).
- Medicinal gels and creams, as well as oral treatment in the form of liquid drugs or pills.
The doctor will evaluate which treatment is most appropriate in each individual case, or assess whether it is best to leave them without treatment. It all depends on the baby, the number of mollusks, their spread and what symptoms they give.
What to do if your child has molluscum contagiosum (MC)
If your child has this infection, you can take several precautions to avoid spreading it to others. It also prevents it from spreading to the rest of your baby’s body.
Some of these measures are:
- Avoid touching, tearing or rubbing the mollusks as much as possible.
- Avoid using the same things, such as clothes, sheets and towels, as people who are not infected.
- Wash your hands often and also keep the affected area clean and dry.
In addition to these measures, a child with molluscum contagiosum can continue to live a completely normal life. For example, still go out and play with other children.
However, we would like to mention that even if the infection has healed and there are no mollusks left, a person can become infected and suffer from it again. Therefore, people who have already been affected in the past should also take these preventive measures.
In summary
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin condition that usually does not cause complications and in most cases disappears on its own or with the help of some simple treatment. In case of injuries or symptoms, it is important, as always, to take your child to a doctor so that he or she can make the final diagnosis and decide on the most appropriate treatment.